Table of Contents
In this article, we will see how to install bluefish text editor on Ubuntu 20.04. Bluefish is a powerful text editor targeted towards programmers and web developers, offering a wide range of tools and features for editing code and markup languages. It is known for its versatility, supporting numerous programming and scripting languages, and for its performance, being able to handle large files and multiple documents with ease. Bluefish is designed to be lightweight and fast, capable of opening and editing files with hundreds of thousands of lines without significant lag.
It allows users to work with multiple files in a single window, facilitating multitasking and navigation between documents. Bluefish is available on various operating systems, including Linux, FreeBSD, macOS, Solaris, and Windows. Here we will see the steps to install Bluefish text editor on Ubuntu 20.04 based systems.
Important Features
- Multi-Language Support: Bluefish supports a wide range of programming and scripting languages, including HTML, CSS, XML, PHP, C, C++, JavaScript, Java, Python, Perl, Ruby, SQL, and many more.
- Syntax Highlighting and Code Folding: The editor provides syntax highlighting, making it easier to read code, and code folding for better navigation of large sections of code.
- Project Management: Bluefish includes features for managing complex projects, allowing users to organize files and folders, and integrate with version control systems.
- Search and Replace: It offers powerful search and replace functionalities, including the ability to handle multiple files and directories, and support for regular expressions.
- Snippets and Auto-Completion: The editor provides snippets and auto-completion for many programming languages, speeding up the coding process.
- Integration with External Programs: Bluefish can integrate with external programs and systems, like web browsers for previewing web pages, or compilers for programming languages.
- Customizability: Users can customize the interface and functionality to a large extent, tailoring the editor to their specific needs.
- Remote File Editing: Bluefish supports editing files directly over protocols like FTP, SFTP, HTTP, HTTPS, WebDAV, and more.
- Unicode Support: It offers full Unicode support, including UTF-8, which is essential for working with internationalized content.

How to Install Bluefish Text Editor on Ubuntu 20.04
Also Read: How to Install GNOME Tweak tool on Ubuntu 22.04
Step 1: Prerequisites
a) You should have a running Ubuntu 20.04 Server.
b) You should have sudo or root access to run privileged commands.
c) You should have apt or apt-get utility available in your Server.
d) You may also need to have tar, wget and make utility available in your system in case you would like to install bluefish using source code.
Step 2: Update Your Server
To keep system stable and secure, it is always recommended to check and install all latest available security fixes and upgrades from ubuntu repo by using sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
Hit:1 http://ppa.launchpad.net/flatpak/stable/ubuntu focal InRelease
Hit:2 https://d3nt0h4h6pmmc4.cloudfront.net/ubuntu focal InRelease
Ign:3 https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ InRelease
Hit:4 http://ppa.launchpad.net/gencfsm/ppa/ubuntu focal InRelease
Hit:5 https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ Release
Get:6 https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu focal InRelease [8,041 B]
Hit:7 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal InRelease
Get:8 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security InRelease [114 kB]
Hit:9 http://ppa.launchpad.net/juju/stable/ubuntu focal InRelease
Get:10 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates InRelease [114 kB]
Hit:11 http://ppa.launchpad.net/libreoffice/ppa/ubuntu focal InRelease
Hit:12 https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/apt/focal pgadmin4 InRelease
Hit:13 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable InRelease
Hit:14 http://ppa.launchpad.net/linuxuprising/guake/ubuntu focal InRelease
........................................................
Step 3: Install Bluefish
In the next step, you can install bluefish by using any of the below methods depending on your needs and requirements.
a) Using default repo
The most easiest way to install bluefish is from default Ubuntu repo using apt or apt-get package manager. You just have to run sudo apt install bluefish command as shown below. This will download and install the package along with all its required dependencies.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install bluefish [sudo] password for cyberithub: Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: bluefish-data bluefish-plugins enchant libenchant1c2a libgucharmap-2-90-7 Suggested packages: csstidy dos2unix php-codesniffer pylint tidy weblint-perl | weblint libenchant-voikko The following NEW packages will be installed: bluefish bluefish-data bluefish-plugins enchant libenchant1c2a libgucharmap-2-90-7 0 upgraded, 6 newly installed, 0 to remove and 17 not upgraded. Need to get 4,026 kB of archives. After this operation, 15.7 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y Get:1 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 bluefish-data all 2.2.11-1 [2,383 kB] Get:2 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 libgucharmap-2-90-7 amd64 1:13.0.1-1 [1,106 kB] Get:3 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 bluefish-plugins amd64 2.2.11-1 [177 kB] Get:4 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 libenchant1c2a amd64 1.6.0-11.3build1 [64.7 kB] Get:5 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 bluefish amd64 2.2.11-1 [284 kB] Get:6 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 enchant amd64 1.6.0-11.3build1 [12.4 kB] Fetched 4,026 kB in 2s (2,050 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package bluefish-data. ....................................................................
b) Using aptitude
Alternatively, you also have the option to install bluefish through aptitude package manager. You just need to run sudo aptitude install bluefish command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo aptitude install bluefish The following NEW packages will be installed: bluefish bluefish-data{a} bluefish-plugins{a} enchant{a} libenchant1c2a{a} libgucharmap-2-90-7{a} 0 packages upgraded, 6 newly installed, 0 to remove and 7 not upgraded. Need to get 4,026 kB of archives. After unpacking 15.7 MB will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n/?] Y Get: 1 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 bluefish-data all 2.2.11-1 [2,383 kB] Get: 2 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 libgucharmap-2-90-7 amd64 1:13.0.1-1 [1,106 kB] Get: 3 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 bluefish-plugins amd64 2.2.11-1 [177 kB] Get: 4 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 libenchant1c2a amd64 1.6.0-11.3build1 [64.7 kB] Get: 5 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 bluefish amd64 2.2.11-1 [284 kB] Get: 6 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 enchant amd64 1.6.0-11.3build1 [12.4 kB] Fetched 4,026 kB in 3s (1,507 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package bluefish-data. (Reading database ... 296172 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../0-bluefish-data_2.2.11-1_all.deb ... Unpacking bluefish-data (2.2.11-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libgucharmap-2-90-7:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../1-libgucharmap-2-90-7_1%3a13.0.1-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libgucharmap-2-90-7:amd64 (1:13.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package bluefish-plugins:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../2-bluefish-plugins_2.2.11-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking bluefish-plugins:amd64 (2.2.11-1) ...
c) Using Source Code
Another method you can use to install bluefish is through source code. For that, you have to first download the latest source code from official website using wget utility as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ wget https://www.bennewitz.com/bluefish/stable/source/bluefish-2.2.14.tar.gz --2024-01-22 02:11:57-- https://www.bennewitz.com/bluefish/stable/source/bluefish-2.2.14.tar.gz Resolving www.bennewitz.com (www.bennewitz.com)... 88.99.103.46 Connecting to www.bennewitz.com (www.bennewitz.com)|88.99.103.46|:443... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 6358892 (6.1M) [application/x-gzip] Saving to: ‘bluefish-2.2.14.tar.gz’ bluefish-2.2.14.tar.gz 100%[============================================================================>] 6.06M 2.31MB/s in 2.6s 2024-01-22 02:12:01 (2.31 MB/s) - ‘bluefish-2.2.14.tar.gz’ saved [6358892/6358892]
Then extract the tarball using tar -xzf bluefish-2.2.14.tar.gz command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ tar -xzf bluefish-2.2.14.tar.gz
Switch to the directory using cd bluefish-2.2.14 command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ cd bluefish-2.2.14
Then run configure script to check the system configuration and prepare it for installation.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~/bluefish-2.2.14$ ./configure
checking for a BSD-compatible install... /usr/bin/install -c
checking whether build environment is sane... yes
checking for a thread-safe mkdir -p... /usr/bin/mkdir -p
checking for gawk... gawk
checking whether make sets $(MAKE)... yes
checking whether make supports nested variables... yes
checking build system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
checking host system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
checking whether to enable maintainer-specific portions of Makefiles... no
checking for a sed that does not truncate output... /usr/bin/sed
checking whether NLS is requested... yes
checking for msgfmt... /usr/bin/msgfmt
checking for gmsgfmt... /usr/bin/msgfmt
checking for xgettext... /usr/bin/xgettext
.........................................
Once configuration is checked, compile the source code and generate binaries using make command. This will read the instructions from Makefile and compile the source code in that order.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~/bluefish-2.2.14$ make
Finally, install all the binaries by using sudo make install command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~/bluefish-2.2.14$ sudo make install
Step 4: Check Version
You can check the current installed version by using bluefish --version command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ bluefish --version Bluefish Editor 2.2.11
Step 5: Verify Installation
If you installed bluefish through apt or aptitude package manager then you can verify the installation status by running dpkg -s bluefish command as shown below. To know more about dpkg command usage, check 21+ Practical dpkg Command Examples for Linux Beginners.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ dpkg -s bluefish Package: bluefish Status: install ok installed Priority: optional Section: web Installed-Size: 854 Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <ubuntu-devel-discuss@lists.ubuntu.com> Architecture: amd64 Version: 2.2.11-1 Depends: bluefish-data (= 2.2.11-1), bluefish-plugins (= 2.2.11-1), gvfs-backends, libc6 (>= 2.14), libcairo2 (>= 1.10.0), libenchant1c2a (>= 1.6.0), libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0 (>= 2.22.0), libglib2.0-0 (>= 2.37.3), libgtk-3-0 (>= 3.21.5), libpango-1.0-0 (>= 1.22.0), libpangocairo-1.0-0 (>= 1.14.0), libxml2 (>= 2.7.4) Suggests: csstidy, dos2unix, libxml2-utils, php-codesniffer, pylint, tidy, weblint-perl | weblint, www-browser .......................................................
Step 6: Launch Bluefish
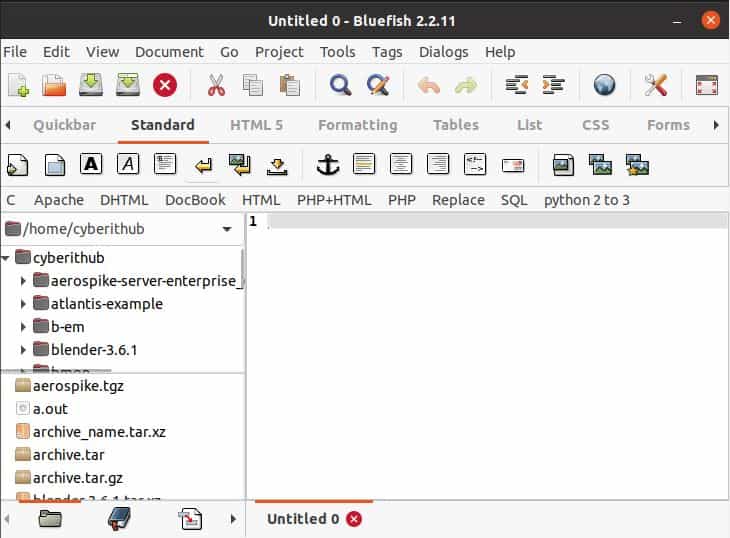
To launch bluefish editor, go to Activities and search bluefish in the search bar as shown below. As soon as it appears, tap on it to open.

When you open it for the first time after installation then it should display like below. You can now start using the text editor for your tasks.
Step 7: Uninstall Bluefish
Once you are done using Bluefish text editor, you can choose to uninstall it from your system by using any of the below methods depending on how you installed it.
a) Using apt or apt-get
If you installed bluefish through apt or apt-get package manager then you can uninstall it by running sudo apt remove bluefish command as shown below. To remove all dependencies, use --auto-remove option with below command.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt remove bluefish [sudo] password for cyberithub: Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: bluefish-data bluefish-plugins enchant libenchant1c2a libgucharmap-2-90-7 Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them. The following packages will be REMOVED: bluefish 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 1 to remove and 17 not upgraded. After this operation, 874 kB disk space will be freed. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y (Reading database ... 296600 files and directories currently installed.) Removing bluefish (2.2.11-1) ... Processing triggers for mime-support (3.64ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.36.0-1ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) ... Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.24-1ubuntu3) ...
b) Using aptitude
If you installed bluefish using aptitude package manager, then to uninstall run sudo aptitude remove bluefish command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo aptitude remove bluefish The following packages will be REMOVED: bluefish bluefish-data{u} bluefish-plugins{u} enchant{u} libenchant1c2a{u} libgucharmap-2-90-7{u} 0 packages upgraded, 0 newly installed, 6 to remove and 7 not upgraded. Need to get 0 B of archives. After unpacking 15.7 MB will be freed. Do you want to continue? [Y/n/?] Y (Reading database ... 296669 files and directories currently installed.) Removing bluefish (2.2.11-1) ... Removing bluefish-data (2.2.11-1) ... Removing bluefish-plugins:amd64 (2.2.11-1) ... Removing enchant (1.6.0-11.3build1) ... Removing libenchant1c2a:amd64 (1.6.0-11.3build1) ... Removing libgucharmap-2-90-7:amd64 (1:13.0.1-1) ... Processing triggers for mime-support (3.64ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for hicolor-icon-theme (0.17-2) ... Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.36.0-1ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.31-0ubuntu9.14) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) ... Processing triggers for shared-mime-info (1.15-1) ... Processing triggers for sgml-base (1.29.1) ... Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.24-1ubuntu3) ...
