Table of Contents
In this tutorial, we will discuss the implementation of OSPF dynamic routing protocol on Cisco routers. This tutorial is intended to guide you in implementing a popular IGP dynamic routing protocol known as OSPF (open shortest path first).
Overview
To forward data from a source to a destination, routers have to use certain mechanisms. There are two major classifications of routing techniques used in most networks today, they are Static and Dynamic routing. Static routing involves the use of predetermined values that are present in the routing tables of the routers.
Conversely, dynamic routing is a configuration that enables efficient routing of data when a router is connected to multiple networks. The router does this by adjusting automatically in response to changes in network topology. It actively learns about routing information and adds the best route to its table.
Routing protocols can also refer to broader standards surrounding these routing techniques. Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) and Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGP) are two major classifications of dynamic routing protocols. I am assuming you are familiar with basic networking terms and principles. If not, then check An Introduction to Basic Networking Concepts and Principles to get familiar with.
What is OSPF
OSPF is a classless, IGP dynamic routing protocol. It uses Link State Routing (LSR) algorithm to gather routing information from nearby routers which it uses to build a topology map.
It is open standard making it available to multiple vendors. And it is widely used in the implementation of LAN networks.
Other examples of IGP routing protocols include :-
- Routing Information Gateway (RIP)
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Protocol (EIGP)
- Intermediate System to Intermediate System (ISIS)
Why is it so Popular
Each routing protocol has its strengths and weaknesses, however, OSPF is widely used for several reasons including :-
- It has support for IPv4 and IPv6
- It has unlimited hop counts
- Classless protocol
- Trigger updates for quick convergence
Other features include :-
- an administrative distance of 110.
- a multicast address of 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6 for communication between neighbors in a single network.
Important terms
Before we go into setting up the OSPF protocol there are some important concepts relating to its operation you need to know.
They include:
- OSPF neighbors: routers configured to use OSPF need to implement a relationship before they can exchange routing tables. They store info about their neighbors in a neighbor table.
- OSPF routers use a technique known as Shortest Path First (SPF) to calculate optimal routes to take from a source to a destination. This info is stored in its routing table.
- OSPF areas: the routers are grouped logically to form OSPF areas. Routers in the same area have the same area ID and topology table.
With much of that out of the way, let's get down to implementation!

How to Implement OSPF dynamic routing protocol on Cisco routers
Also Read: What is BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) | Explained with example
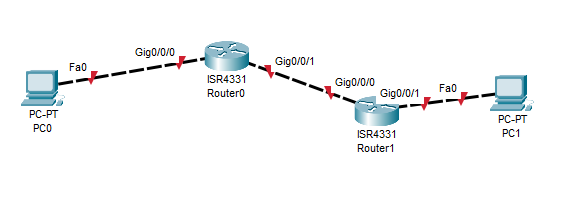
We need to first setup our network. For that we are going to use a basic network of 2 host devices and 2 routers. But even before that we need to first set up our devices.
 For the sake of simplicity:-
For the sake of simplicity:-
FastEthernet 0 - fa/0
GigabitEthernet 0/0 - g0/0
GigabitEthernet 0/0 - g0/1
Steps to connect interfaces :-
- Connect the fa/0 port of PC0 to g0/0 of router0
- Connect the g0/1 of router 0 to g0/1 of router1
- Connect the g0/0 of router1 to the fa/0 of PC1
To use these devices, we have to assign IP addresses to them, then we turn the interfaces on.
a) Configuring the devices
We begin with the routers. Click on the routers and assign IP addresses to their interfaces.
For router0,
- set IP address of g0/0 to 20.0.0.1 and
- set g0/1 to 30.0.0.1
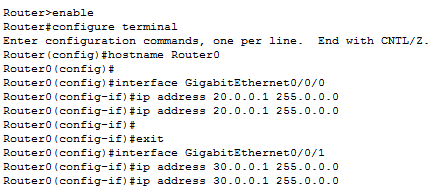
We can turn its interfaces on using the no shutdown command.

Repeat a similar process for router1.
- Set its g0/0 to 40.0.0.1 and
- g0/1 to 30.0.0.2 ( same network as router0's g0/1 interface).
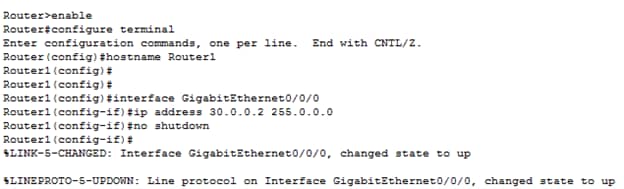
Next, set and turn the interface on for g0/1.

b) PC0 and PC1
Go to IP configuration from Desktop menu.
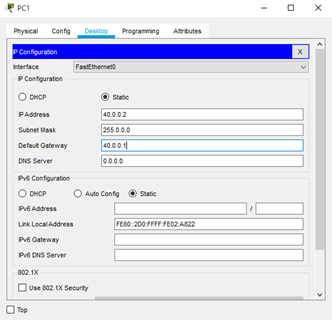
Since PC0 is connected to router0's interface we set it's
- IP address to 20.0.0.2 and
- Default gateway to 20.0.0.1 (Router0's IP address).
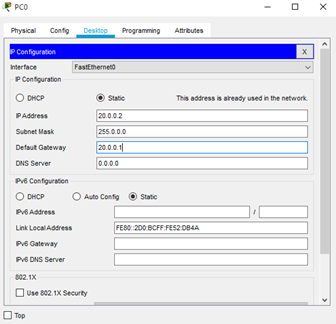
For PC1, set its
- IP address to 40.0.0.2 and
- Default gateway to 40.0.0.1
After doing the above, the network should look similar to this.
Now we test the network to confirm connectivity. We do this using the ping command from PC0's terminal.
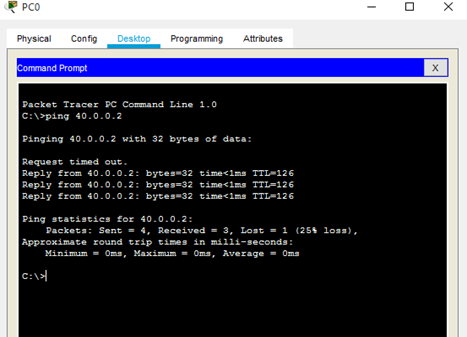
Great! Now let's set up OSPF.
c) Setting up OSPF protocol
There are two important commands needed to configure our routers to use OSPF.
- router ospf <ID>
- network <IP> <WILDCARD> <MASK> <AREA> <CODE>
The area code should be the same value for both routers. We will be using 1 as the area code.
d) Wild card masks
Wild card masks are similar to subnet masks in that they are used for matching bits in network addresses using an AND operation. But unlike subnetting, wild card masks reverse the significance of 0s and 1s.
0 = match bits. 1 = ignore.
For instance, assuming we have a network 198.172.50.0 with a wild card mask of 0.0.0.255. The resultant addresses from this masking must match the bits in the first 3 octets.
Therefore, valid addresses are 198.172.50.0 - 198.172.50.255.
The wild card mask is used in OSPF to mitigate the limitations of classful protocols which can not tell the difference between networks.
e) Configure OSPF
From Router0's global config mode, enter the ospf commands.
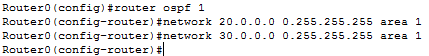
Do the same for Router1
![]()
And that's it. Next, we need to verify that our setup was successful. We can do this using the show ip ospf neighbor command.
For Router0,
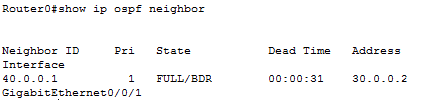
For Router1,

So we are good.
We can verify IP route using the show ospf ip route command.

And that is all. We have successfully configured our routers for OSPF dynamic routing protocol.
Reference:-
"Dynamic Routing Protocols: OSPF, EIGRP, RIPv2, IS-IS, BGP". Cisco. Retrieved September 11, 2022.

thanks alot of information!!