Table of Contents
In this article, I will take you through the steps to install Wireshark on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa). Wireshark is a free protocol and network packet analyzing tool. It is known as the world's most widely used network protocol analyzer. It first captures the data from a network interface and then breaks the capture into the frames, segments, and packets for further analysis.
You can analyze the packets immediately or save it in a file to analyze it later. You can also share the captured packet to others in wireshark format. More on official website. Wireshark can be easily installed in all of the famous operating systems but here we are going to look into the steps to install wireshark on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS System.
Important Features
- It supports deep inspection of hundreds of protocols, with more and more being added all the time.
- It allows us to perform Live packet as well as offline analysis
- It has standard three-pane packet browser
- It can easily run on platforms like Windows, Linux, macOS, Solaris, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and many others.
- You can easily browse Captured network data via a GUI, or via the TTY-mode TShark utility.
- It has the most powerful display filters
- It has Rich set of VoIP analysis features.
- It can read/write many different capture file formats including tcpdump (libpcap), Pcap NG etc.
- It can capture files compressed with gzip and can also be decompressed on the fly.
- It can be used to read live data from Ethernet, IEEE 802.11, PPP/HDLC, ATM, Bluetooth, USB, Token Ring, Frame Relay, FDDI, and others (depending on your platform).
- It has decryption support for many protocols, including IPsec, ISAKMP, Kerberos, SNMPv3, SSL/TLS, WEP, and WPA/WPA2
- You can utilize the coloring rules to the packet list for quick and intuitive analysis.
- The output can be easily exported to XML, PostScript®, CSV, or plain text.

How to Install Wireshark on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa)
Also Read: How to Install GitKraken Client on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa)
Step 1: Prerequisites
a) You should have a running Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Server.
b) You should have sudo or root access to run privileged commands.
c) You should have apt or apt-get utility available in your System.
Step 2: Update Your Server
In the first step, you need to sync all the installed packages with the latest available versions from the default Ubuntu repo by using sudo apt update command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt update
Hit:1 https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu focal InRelease
Hit:2 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable InRelease
Get:3 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security InRelease [114 kB]
Hit:4 http://ppa.launchpad.net/ubuntu-toolchain-r/test/ubuntu focal InRelease
Hit:5 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal InRelease
Get:6 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates InRelease [114 kB]
Hit:7 https://apt.boltops.com stable InRelease
Get:8 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security/main amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [40.7 kB]
Get:9 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports InRelease [108 kB]
Get:10 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security/universe amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [92.7 kB]
Get:11 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security/multiverse amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [2,468 B]
Get:12 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main amd64 Packages [2,158 kB]
Get:13 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main i386 Packages [738 kB]
Get:14 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [277 kB]
Get:15 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/universe amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [405 kB]
Get:16 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/multiverse amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [944 B]
Get:17 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports/main amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [7,964 B]
Get:18 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports/universe amd64 DEP-11 Metadata [30.5 kB]
Fetched 4,090 kB in 4s (1,066 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
All packages are up to date.
You can also run upgrade once using sudo apt upgrade command to check if any of the installed packages needs to be upgraded.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt upgrade
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
Calculating upgrade... Done
Try Ubuntu Pro beta with a free personal subscription on up to 5 machines.
Learn more at https://ubuntu.com/pro
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Step 3: Install Wireshark
There are multiple ways to install wireshark on Ubuntu system. You can choose any of the below method depending on whichever works best for you.
a) Using apt or apt-get
If you are looking to install wireshark package from default Ubuntu repo then you need to use sudo apt install wireshark command as shown below. This will download and install the package along with all its dependencies.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install wireshark Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: libc-ares2 liblua5.2-0 libqt5printsupport5 libsmi2ldbl libspandsp2 libwireshark-data libwireshark13 libwiretap10 libwsutil11 wireshark-common wireshark-qt Suggested packages: snmp-mibs-downloader geoipupdate geoip-database geoip-database-extra libjs-leaflet libjs-leaflet.markercluster wireshark-doc The following NEW packages will be installed: libc-ares2 liblua5.2-0 libqt5printsupport5 libsmi2ldbl libspandsp2 libwireshark-data libwireshark13 libwiretap10 libwsutil11 wireshark wireshark-common wireshark-qt 0 upgraded, 12 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 21.8 MB of archives. After this operation, 115 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y ...................................................
b) Using PPA repository
If you are looking to install wireshark from PPA repository then you need to first add the repository using below add-apt-repository command.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:wireshark-dev/stable
[sudo] password for cyberithub:
Latest stable Wireshark releases back-ported from Debian package versions.
Back-porting script is available at https://github.com/rbalint/pkg-wireshark-ubuntu-ppa
From Ubuntu 16.04 you also need to enable "universe" repository, see:
http://askubuntu.com/questions/148638/how-do-i-enable-the-universe-repository
The packaging repository for Debian and Ubuntu is at: https://salsa.debian.org/debian/wireshark
More info: https://launchpad.net/~wireshark-dev/+archive/ubuntu/stable
Press [ENTER] to continue or Ctrl-c to cancel adding it.
Hit:1 https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu focal InRelease
Hit:2 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable InRelease
Hit:3 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal InRelease
Hit:4 http://ppa.launchpad.net/ubuntu-toolchain-r/test/ubuntu focal InRelease
..............................................
Then you need to update the system cache using sudo apt update command as shown below. This will make system aware of the recently added PPA repository.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt update Hit:1 https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu focal InRelease Hit:2 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable InRelease Hit:3 http://ppa.launchpad.net/ubuntu-toolchain-r/test/ubuntu focal InRelease Hit:4 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security InRelease Hit:5 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal InRelease Hit:6 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates InRelease Hit:7 http://ppa.launchpad.net/wireshark-dev/stable/ubuntu focal InRelease Hit:8 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports InRelease Hit:9 https://apt.boltops.com stable InRelease Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done
Now you can install the package from PPA repository by using sudo apt install wireshark command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install wireshark Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: libc-ares2 liblua5.2-0 libminizip1 libqt5printsupport5 libsmi2ldbl libspandsp2 libwireshark-data libwireshark15 libwiretap12 libwsutil13 wireshark-common wireshark-qt Suggested packages: snmp-mibs-downloader geoipupdate geoip-database geoip-database-extra libjs-leaflet libjs-leaflet.markercluster wireshark-doc The following NEW packages will be installed: libc-ares2 liblua5.2-0 libminizip1 libqt5printsupport5 libsmi2ldbl libspandsp2 libwireshark-data libwireshark15 libwiretap12 libwsutil13 wireshark wireshark-common wireshark-qt 0 upgraded, 13 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 24.3 MB of archives. After this operation, 129 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y Get:1 http://ppa.launchpad.net/wireshark-dev/stable/ubuntu focal/main amd64 libwireshark-data all 3.6.7-1~ubuntu20.04.0+wiresharkdevstable [1,589 kB] .........................................................
Step 4: Check Version
Once wireshark is successfully installed, you can test its installation by using wireshark --version command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ wireshark --version Wireshark 3.2.3 (Git v3.2.3 packaged as 3.2.3-1) Copyright 1998-2020 Gerald Combs <gerald@wireshark.org> and contributors. License GPLv2+: GNU GPL version 2 or later <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-2.0.html> This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Compiled (64-bit) with Qt 5.12.8, with libpcap, with POSIX capabilities (Linux), with libnl 3, with GLib 2.64.2, with zlib 1.2.11, with SMI 0.4.8, with c-ares 1.15.0, with Lua 5.2.4, with GnuTLS 3.6.13 and PKCS #11 support, with Gcrypt 1.8.5, with MIT Kerberos, with MaxMind DB resolver, with nghttp2 1.40.0, with brotli, with LZ4, with Zstandard, with Snappy, with libxml2 2.9.10, with QtMultimedia, without automatic updates, with SpeexDSP (using system library), with SBC, with SpanDSP, without bcg729. Running on Linux 5.15.0-50-generic, with Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-1035G1 CPU @ 1.00GHz (with SSE4.2), with 1976 MB of physical memory, with locale en_IN, with libpcap version 1.9.1 (with TPACKET_V3), with GnuTLS 3.6.13, with Gcrypt 1.8.5, with brotli 1.0.7, with zlib 1.2.11, binary plugins supported (0 loaded). Built using gcc 9.3.0.
Step 5: Reconfigure Wireshark (Optional)
This is an optional step which you only needs to do when you would like to give access to non-superusers to able to capture packets. To provide the access, you need to reconfigure wireshark by running sudo dpkg-reconfigure wireshark-common command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo dpkg-reconfigure wireshark-common
[sudo] password for cyberithub:
You will see below question will pop up where it will ask you select either Yes or No. This needs to be set as Yes by pressing Tab and then press Enter to confirm.
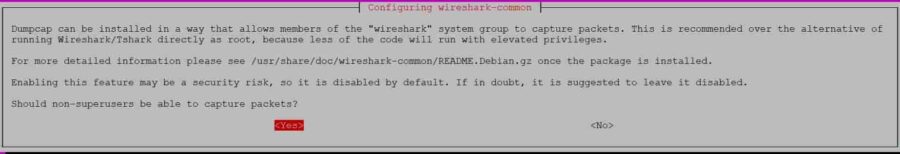
Next, you need to add the user to the Wireshark group by using sudo usermod -a -G wireshark <username> syntax. Since here we are going to capture packets from user cyberithub so we will add this user to the wireshark group as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo usermod -a -G wireshark cyberithub
Finally, you need to provide execute permission to dumpcap using sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/dumpcap command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/dumpcap
Once done, logout to the system and login again to allow the system to read updated changes.
Step 6: Launch Wireshark
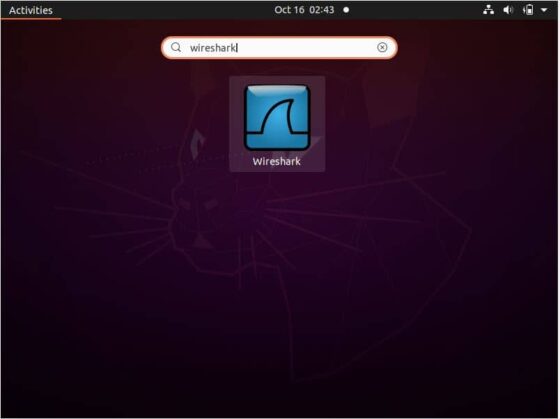
You need to go to Activities and search wireshark in the search box as shown below. Once it shows up, click on it to launch.
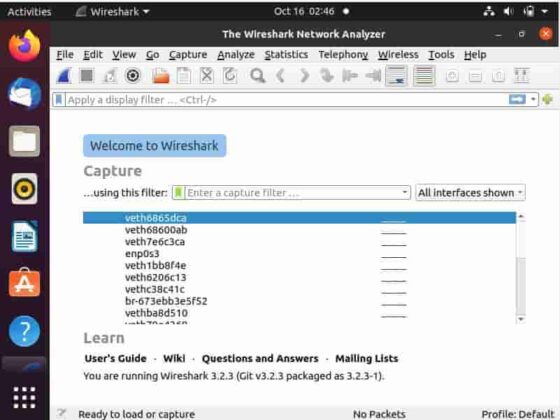
It should open like below with list of interfaces shown. You can select interface on which you would like to capture packets.
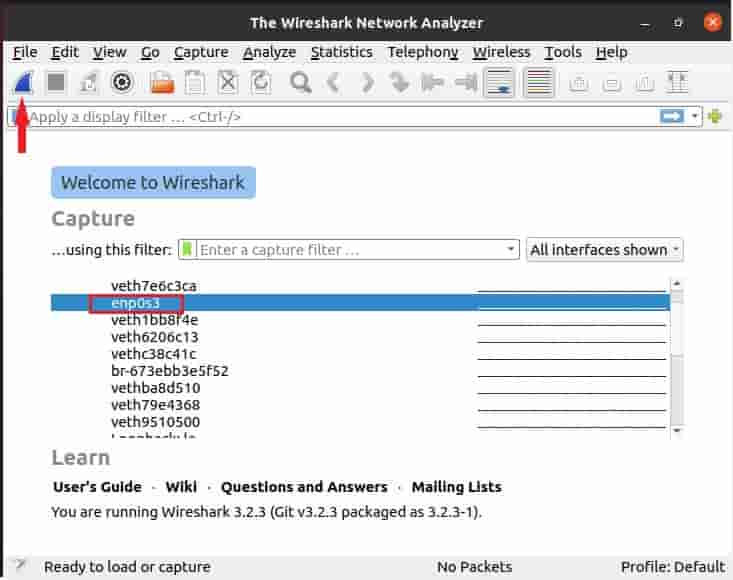
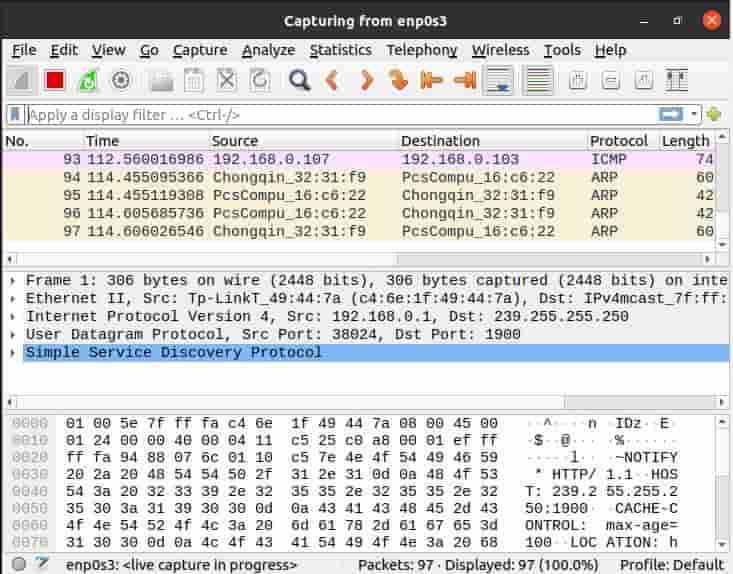
In our case, we are selecting interface enp0s3 as shown below and then we are selecting capture packets.
The packets will start getting captured. You will see live capture in progress as shown below.
Step 7: Uninstall Wireshark
Once you are done using wireshark, you can choose to uninstall it from your System by using sudo apt remove wireshark command as shown below. But before running below command please check for any unwanted package removal as sometimes it might remove some of the packages which are critical for running other applications. Hence it is important to verify below command especially when you are running this on a production or a critical system.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt remove wireshark Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: libc-ares2 liblua5.2-0 libqt5printsupport5 libsmi2ldbl libspandsp2 libwireshark-data libwireshark13 libwiretap10 libwsutil11 wireshark-common wireshark-qt Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them. The following packages will be REMOVED: wireshark 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 1 to remove and 0 not upgraded. After this operation, 59.4 kB disk space will be freed. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y (Reading database ... 257280 files and directories currently installed.) Removing wireshark (3.2.3-1) ...
