Table of Contents
In this article, we will focus on Integration Testing and will try to see when to use Integration testing and what are different integration test approaches to take. As you probably know, unit testing mostly focuses on each and every individual components being developed for the System. Only after removing all the possible defects and making sure the test cases do not reveal any new defects, the components are integrated into a large subsystems.
But at this point, the components can be faulty. This is simply because the test stubs and drivers used during unit testing are possible estimates of the component they simulate. Additionally, unit testing does not show any defects associated with the component interfaces. This is because of the wrong assumptions may be done during calling of the interfaces. So for revealing all those defects, an integration testing has to performed. We will see more about integration testing in below section.

What is Integration Testing: Different Integration Test Approaches
Also Read: Introduction to Client-side Performance Testing [Explained with examples]
Integration testing helps uncovers all those defects that went undetected in the unit testing. It uncovers by focusing on the interfaces between small groups of components. These components could be code modules, client and server based applications or it could even be a single application.
The integration testing initializes only after finishing the unit testing for each module to be integrated is complete. In this type of testing, you will need to have atleast two or more components to be integrated and tested.
Criteria for executing Integration Testing
- Validating the Application Design
- Confirming that the different modules of the application can be successfully integrated to perform one or more application functions.
- Confirming that the application integrates successfully with its environment
Different Integration Test Approaches
Integration testing focuses on multiple test components or modules that works together. Below are the different integration test approaches that can help in conducting the integration testing.
- Big Bang Testing
- Top-down Testing
- Bottom-Up Testing
- Hybrid Testing
We will look into all the integration test approaches one by one.
a) Big Bang Testing
In this approach, all the individual modules or components that passed the unit testing are integrated and tested. This approach is mostly obsolete and hence not much in use as it is only suitable for testing small size software. Developers who follows classical waterfall model sometimes follow this approach. The only benefit in following this approach is that if the unit testing has been thoroughly done for the components then this testing can save lot of time. Also, you do not need to create much stubs and drivers in this model.
In reality, most of the times you will find many errors in this approach and it takes lot of time to rectify those errors in comparison to the errors faced in each module. This testing is also very resource intensive as it requires lot of coordination between the modules to work. Another drawback you will notice in this testing is that you can't begin your testing until all the modules are ready and integrated. This causes a major problem in large software systems. Hence it is not advised to use this approach at all.
b) Top-down Testing
In this approach, the testing basically starts at the top of the hierarchy and travels down to the branches using two different methods - depth-first method and breadth-first method. We will see both the methods in detail.
- Depth-first method: This method involves traversal from the top to all the way down to the lowest level in the hierarchy. All the modules along the path are developed and tested before testing them with the modules on the same level.
- Breadth-first method: This method involves traversal from the top to the next level of the hierarchy. In this method all the modules are developed and tested at the top level first before going to the next level.
Example
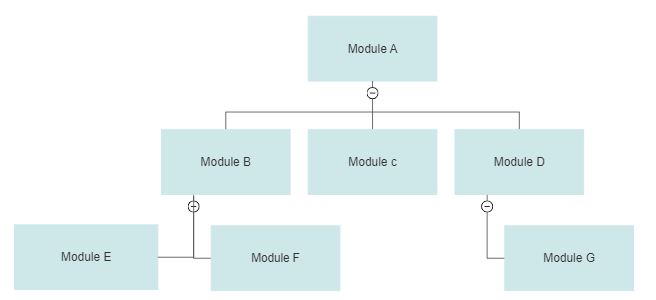
Let's understand the this integration testing through an example module hierarchy as shown below. In the below sequence of integration and testing, Module A is integrated and tested with Module B, Module C and Module D. Then Module E, Module F and Module G are integrated and tested with the units integrated in the first step.
Advantage
- The main advantage of using top-down integration is that it enables you to test the basic skeleton of the system early in the test process. This partially working model can be demonstrated to the clients and the top management. This helps build the confidence of the client and the management in the development team and in the product being developed.
- Sometimes, it proves the correctness of the design and the approach for implementing it.
- Another advantage is that it minimizes the requirements for drivers.
- It helps in testing interfaces early and detect any interface errors at the early stage.
Limitation
- The main limitation of this approach is that it requires program stubs until you write the actual modules.
- Everytime you replace the stub with actual modules, you need to re-test the calling modules for integrity.
c) Bottom-Up Testing
Next is the bottom-up approach. In this approach to integration testing, first the terminal modules are tested in isolation. Then all the lower level modules are integrated and tested with the module at the next upper level. The integrated modules are then tested with each other and see its working. This continuous process of integration and testing with upper level modules goes on till all the modules of the system are tested.
This integration approach does not require program stubs when developing and testing the lower level modules. It mainly focuses on building and testing the critical modules first lies at the bottom of hierarchy and make sure to eradicate all the errors in the early stage of development.
However it is also important to note that since the modules at the low levels are specific to an operation, it may not be required to combine several modules in a cluster and build to test them properly. You just need to write and establish a test driver to test the build.
Example
Let's understand this testing approach by using same module hierarchy as shown earlier. In the below sequence of integration and testing, Module E and Module F are integrated and tested with Module B. Similarly, Module G is integrated and tested with Module D. The hierarchy of the modules under and including Module B, Module C and Module D are integrated and tested with Module A.

Limitation
The main limitation of this integration testing approach is that no working model can be presented or tested until you build lot of modules. This add the risk of detecting interface errors pretty late and hence can complicate the entire test management procedures.
d) Hybrid Testing
In this testing, both top-down and bottom-up approach are applied in parallel. The modules basically divided in two categories - logical and operational. The logical modules are integrated using a top-down approach and operational modules are integrated with bottom-up approach. Then the results of both are converged. This approach minimizes the needs for stubs and drivers. Hybrid testing are mostly used for software that follows waterfall model or incremental software development process model.
